Welding is a demanding and hazardous job requiring adequate protective gear to ensure the welder’s safety and efficiency. Among the essential protective equipment, welding gloves stand out as a critical barrier between your hands and the intense heat, sparks, and metal splatter generated during welding. Choosing the right gloves not only protects your hands but also enhances your dexterity and work quality. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore different types of gloves, materials used, their benefits, tips for selecting the best gloves, and how to maintain them for long-lasting protection.
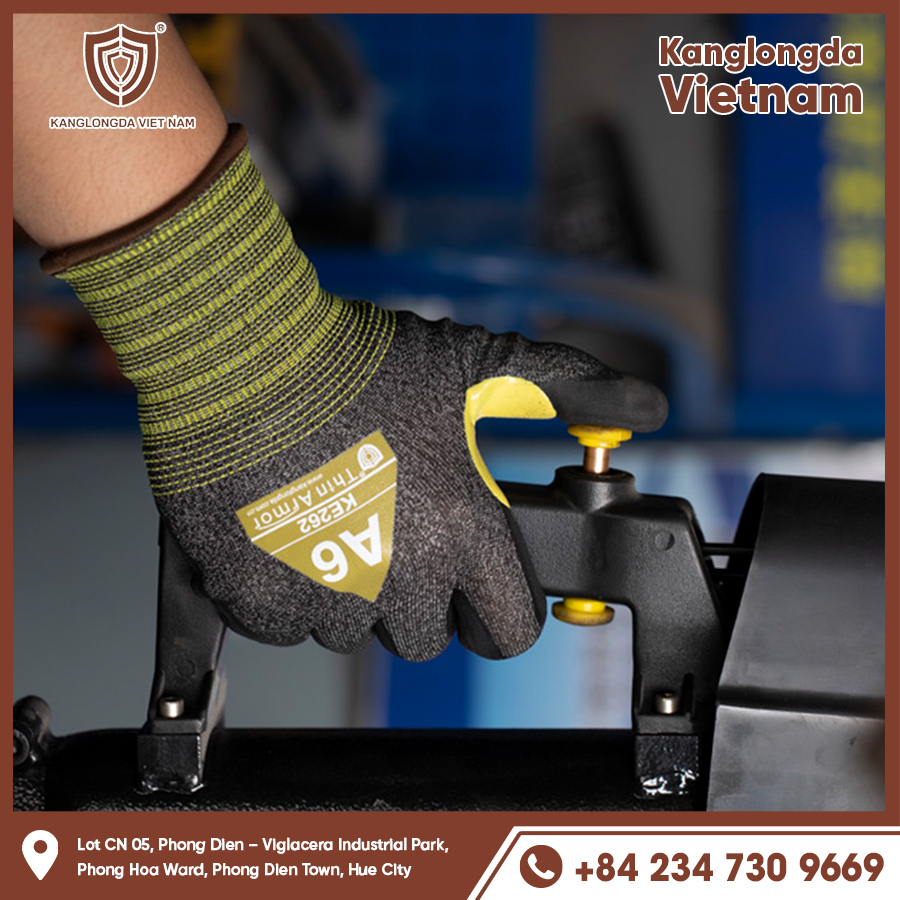

Understanding Welding Gloves
What Are Welding Gloves?
Gloves are specialized protective gloves designed to shield the hands from extreme heat, sparks, molten metal splashes, and electrical shocks encountered during welding processes. Unlike regular gloves, gloves are made from thick, heat-resistant materials such as leather to prevent burns and cuts. They often feature reinforced palms and cuffs to offer extra protection in critical areas. These gloves form a crucial part of personal protective equipment (PPE) for anyone engaged in welding tasks.
Importance of Welding Gloves for Safety
The welding environment exposes workers to severe risks. The extreme temperatures can cause serious burns in seconds. Additionally, sparks and sharp metals can lead to cuts and abrasions. Gloves are specifically engineered to mitigate these risks by providing a heat-insulating and durable barrier. Besides preventing injuries, these gloves also help reduce exposure to harmful UV and infrared radiation emitted during welding, which can cause skin damage over time. Moreover, good gloves improve grip and reduce hand fatigue, enhancing overall productivity and safety on the job.
Key Features of Welding Gloves
Effective gloves should have the following features:
-
Heat resistance to protect against burns and radiant heat.
-
Durability to withstand rough handling and abrasive surfaces.
-
Flexibility and dexterity to handle welding tools precisely without compromising safety.
-
Reinforced palms, fingers, and cuffs for additional protection against sparks and metal splatter.
-
Fire retardant and sometimes moisture resistant properties depending on material composition.
Types of Welding Gloves
MIG Welding Gloves
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding produces moderate heat and sparks. MIG gloves are typically thicker with more padding and insulation to protect against splatter and heat. They offer a good balance between protection and flexibility, allowing welders to manipulate the welding gun and materials effectively. These gloves often feature longer cuffs to shield wrists and lower forearms from sparks. Because MIG welding is commonly used in automotive and manufacturing industries, the gloves need to be durable enough for repetitive tasks while ensuring comfort.
TIG Welding Gloves
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding requires high precision and more finger sensitivity. TIG gloves are thinner and made with softer leather, often goatskin, allowing better dexterity while still providing adequate heat resistance. Since TIG welding is usually applied for more delicate, artistic, or detailed work such as pipe welding or aerospace components, gloves must not hinder tactile feedback. These gloves also tend to have snugger fits and less bulk, sometimes incorporating Kevlar stitching for added heat protection without sacrificing flexibility.
Stick Welding Gloves
Stick welding involves higher heat and more aggressive sparks compared to MIG and TIG. Gloves for this type are usually heavy-duty and constructed with thick cowhide leather, offering maximum protection against burns and electric shock. Stick welding produces more spatter and slag, so gloves used must be resistant to punctures and abrasion. They generally have extra padding on the palms and backs of the hands to absorb impacts and heat. These gloves are typically preferred for heavy industrial welding or outdoor environments.
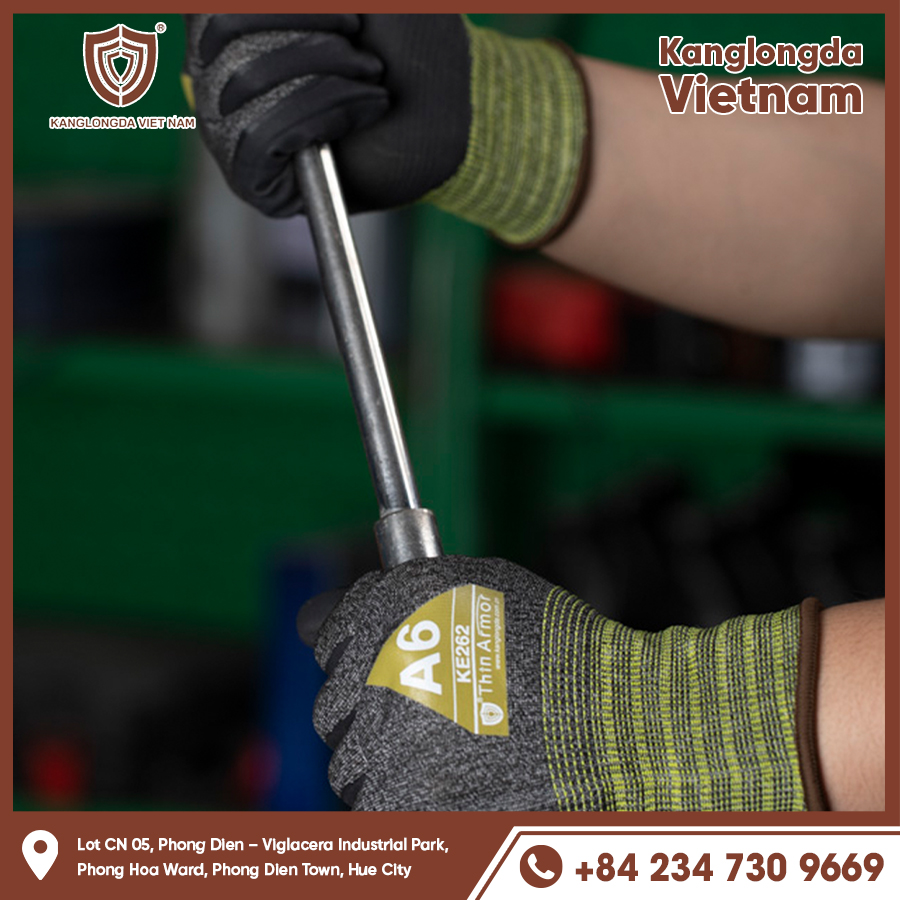

Materials Used in Welding Gloves
Cowhide Leather
Cowhide leather is the most common material for gloves because of its toughness and durability. It is abrasion-resistant and provides excellent protection from heat and sparks, making it ideal for heavy-duty welding applications. Cowhide gloves are typically thicker and stiffer but offer superior resistance against cuts and punctures. They are well-suited for stick welding and other high-heat tasks but might limit some finger mobility compared to other materials.
Goatskin Leather
Goatskin is softer and more flexible than cowhide, which provides greater dexterity for detailed welding tasks like TIG welding. It also offers good heat resistance but is less bulky. Goatskin gloves conform better to the hand shape, allowing better grip and control. This leather is naturally water-resistant, making the gloves comfortable during extended use. However, goatskin gloves might wear faster if used in very abrasive environments.
Pigskin Leather
Pigskin leather is resistant to moisture and heat and maintains durability even when wet. This makes pigskin gloves suitable for outdoor welding or damp environments. Pigskin is moderately flexible and offers excellent abrasion resistance. These gloves are often chosen by welders who need a balance between durability and comfort in varying weather conditions. They may require more break-in time but are highly reliable for long-term use.
Benefits of Welding Gloves
Heat and Flame Protection
Welding gloves are designed to protect hands from extreme temperatures and flames. High-quality gloves can withstand heat exposure without deteriorating quickly, preventing burns and injuries. This is essential because the skin is particularly vulnerable during welding due to direct contact with molten metal and intense radiant heat. Proper gloves ensure safety and help prevent serious occupational injuries.
Enhanced Grip and Control
Good gloves provide a secure grip on tools and materials, which is essential for maintaining precision during welding. The right glove balances protection with tactile feedback. For instance, gloves made with goatskin leather or thinner TIG styles improve finger sensitivity while still providing a heat barrier. This combination of protection and control can increase the quality of welds and reduce mistakes caused by slipping or poor handling.
Increased Comfort and Reduced Fatigue
Gloves with ergonomic design and quality materials reduce hand strain and fatigue. Comfortable gloves allow welders to work for extended periods without discomfort or loss of efficiency. Features such as breathable linings, pre-curved fingers, and flexible leather contribute to better comfort. When hands are comfortable and less fatigued, welders are more productive and safer.
How to Choose the Right Welding Gloves
Match Gloves to Welding Type
Choosing the right glove depends on the welding method you use. For instance, TIG welding demands thinner gloves for more finger control, while stick welding needs thicker gloves for more protection. Understanding the specific hazards of each welding process helps in selecting gloves that optimize both safety and performance. Some gloves are labeled specifically for MIG, TIG, or stick welding, which is a helpful guide for buyers.
Ensure Proper Fit and Size
Gloves should fit snugly without being too tight. A proper fit ensures better dexterity and comfort, reducing the risk of accidents due to slipping or restricted movement. Welders should measure their hand size carefully and try on different brands to find gloves that provide the best balance between flexibility and protection. Oversized gloves can reduce control and increase the chance of catching on equipment.
Check Construction and Durability
Look for gloves with reinforced stitching, double-layered palms, and heat-resistant linings. Quality construction improves glove lifespan and safety during welding. Kevlar or similar fire-resistant threads are preferred for stitching because they resist burning and wear. Additional features like padded palms or adjustable cuffs can enhance glove protection and comfort. Investing in well-made gloves may cost more upfront but reduces replacement frequency and injury risks.
Welding Glove Maintenance and Care
Cleaning Welding Gloves
To extend the life of gloves, clean them regularly. Use mild soap and water for light stains and avoid machine washing unless specified by the manufacturer, as this can damage the leather and lining. After cleaning, let gloves air dry naturally and avoid direct heat sources which can dry out and crack the leather. Regular cleaning removes dirt and oils that degrade material quality.
Inspect for Damage Before Use
Check your gloves before each use for holes, cracks, or worn areas. Damaged gloves compromise safety and should be replaced immediately to prevent injuries. Minor holes can allow sparks and molten metal to penetrate, causing burns. Frequent inspection helps catch wear early and keeps the gloves performing optimally.
Proper Storage Practices
Store gloves in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and chemicals. Avoid folding or crushing them to maintain the glove’s shape and protective properties. Hanging gloves or laying them flat is best. Proper storage prevents premature aging, cracking, or stiffness caused by moisture or environmental factors.
Common Mistakes When Using Welding Gloves
Using Incorrect Gloves for the Job
Using gloves that don’t match your welding type can result in insufficient protection or reduced dexterity, leading to accidents or poor work quality. Always select gloves designed for the specific welding process you perform to ensure the best safety and performance.
Ignoring Glove Damage
Many welders continue to use gloves with visible wear and tear. This negligence increases the risk of burns and cuts and should be avoided. Replacing gloves immediately when damaged is essential for safe welding.
Poor Glove Maintenance
Failing to clean and properly store gloves shortens their lifespan and compromises safety. Neglecting maintenance can lead to hardened leather, reduced flexibility, and vulnerability to hazards.

Welding gloves are an indispensable piece of personal protective equipment for anyone working with welding tools. Understanding the different types, materials, and proper maintenance techniques can help you select the perfect pair for your needs. Always prioritize safety, comfort, and durability when choosing gloves to protect your hands effectively and improve your welding performance. By investing time in choosing the right gloves and taking good care of them, you ensure a safer, more productive welding experience.